Leading the genome
editing revolution
The discovery of CRISPRAdapted from a naturally occurring bacterial immune system, CRISPR is an acronym for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. One of the proteins in the CRISPR system is known as CRISPR-associated 9 protein or Cas9 protein, which cleaves the DNA. Researchers have co-opted the bacterial CRISPR system to make specific changes in the DNA of humans, other animals and plants. CRISPR was first harnessed in 2012 as a genome editing tool in the lab. More recently, scientists have begun engineering and testing CRISPR systems to be very specific to a desired genetic target. by Intellia co-founder Jennifer Doudna and her colleague Emmanuelle Charpentier captured the world’s attention for its potential to revolutionize how we treat disease. That opportunity drives Intellia in its mission to transform the lives of people with severe diseases through curative genomeA genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. In humans, a copy of the entire genome—more than three billion DNA base pairs—is contained in all cells that have a nucleus. editing treatments.

Learn more about our history and join us in the continuing journey toward a new era of medicine.
Intellia Therapeutics Founded
Intellia is founded to transform the lives of people with severe diseases by developing curative genome editing treatments.

Novartis Collaboration Established
Intellia initiates its first collaboration with Novartis to develop novel cell therapies using Intellia’s ex vivo CRISPR/Cas9 platform — marking an important validation of Intellia’s team and capabilities.
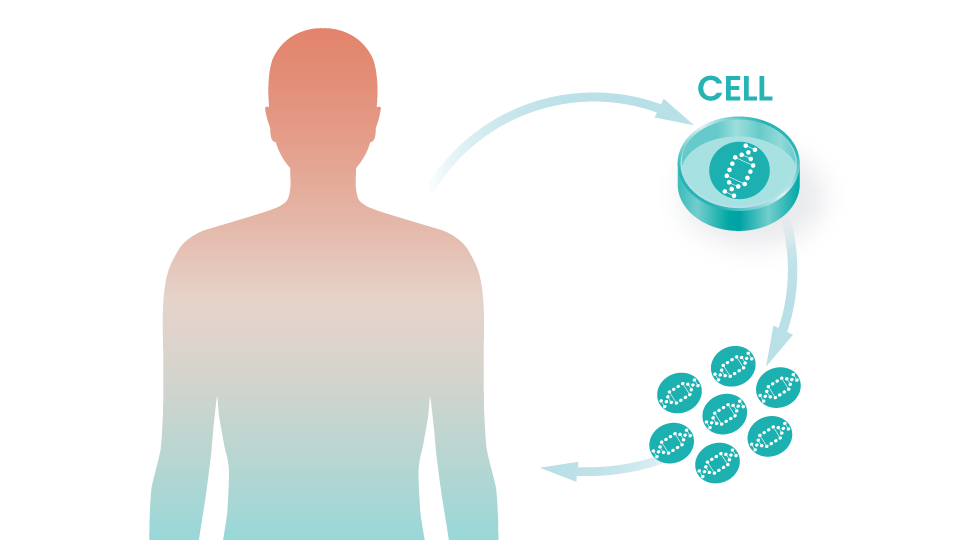
Regeneron Collaboration Began
Intellia begins a collaboration with Regeneron focused on in vivo applications of CRISPR/Cas9. Partnership further expanded in 2020.
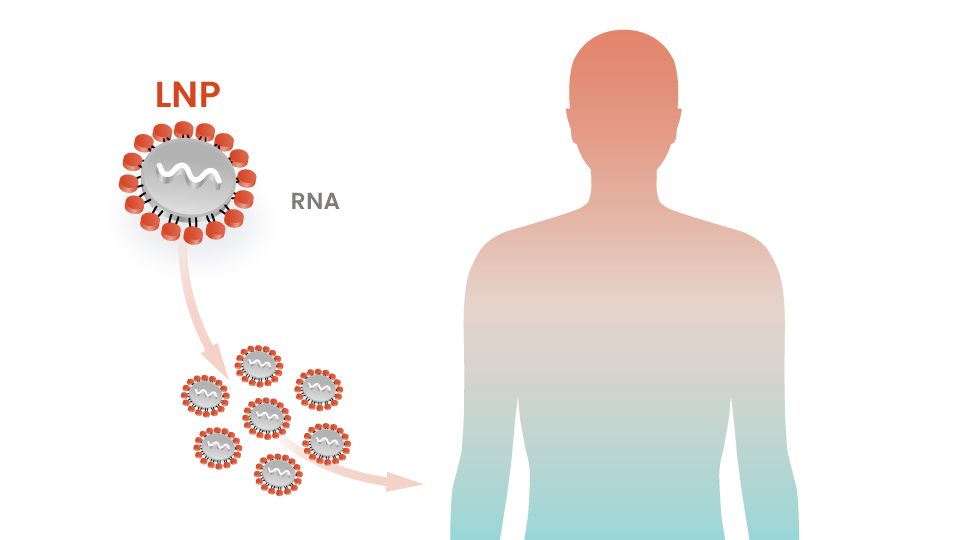
Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Delivery System Established
Intellia demonstrates its foundational proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system in preclinical studies, paving the way to precisely deliver CRISPR/Cas9 to target cells — the central technical challenge to creating potentially curative in vivo genome editing treatments in humans.
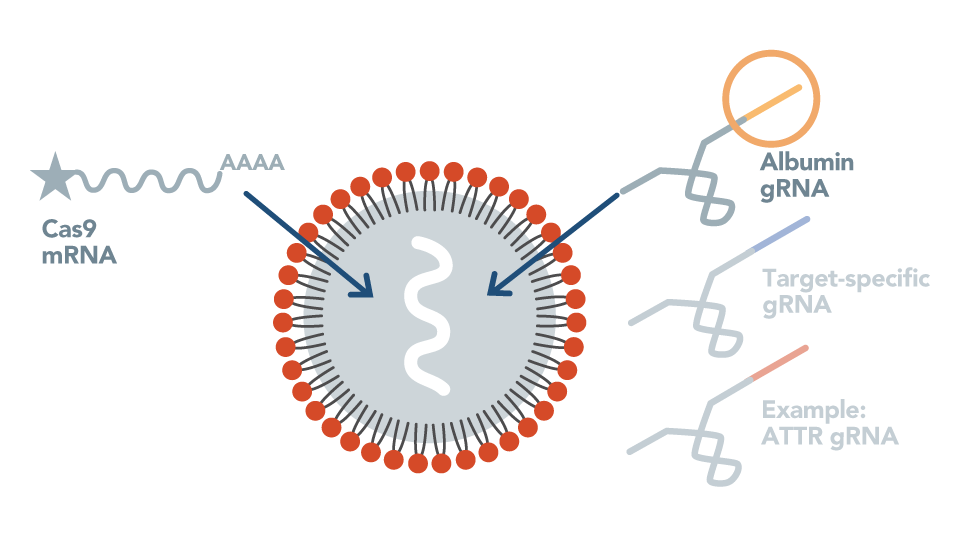
First In Vivo Genome Editing in Non-Human Primates
Intellia demonstrates editing of the TTR gene in liver cells of non-human primates with therapeutically relevant reduction of serum TTR protein.

Nobel Prize Awarded to Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier
Intellia co-founder Jennifer Doudna and colleague Emmanuelle Charpentier win the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of CRISPR/Cas9.

Preclinical Proof of Concept for CRISPR-based In Vivo Editing of Bone Marrow
Intellia demonstrates systemic in vivo genome editing in a tissue outside the liver in preclinical models, supporting the potential for a less invasive treatment of sickle cell disease and other inherited blood disorders and reinforcing the promise of Intellia’s modular platform.
First-Ever Clinical Data for In Vivo CRISPR Genome Editing
Intellia and Regeneron make history by announcing interim Phase 1 data for NTLA-2001, demonstrating the ability to precisely edit target cells within the body to treat genetic disease with a single intravenous infusion of CRISPR. Landmark data published in the New England Journal of Medicine in August 2021.

FDA clearance of IND application for NTLA-2002
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared the company’s Investigational New Drug (IND) application for NTLA-2002 for the treatment of hereditary angioedema (HAE).
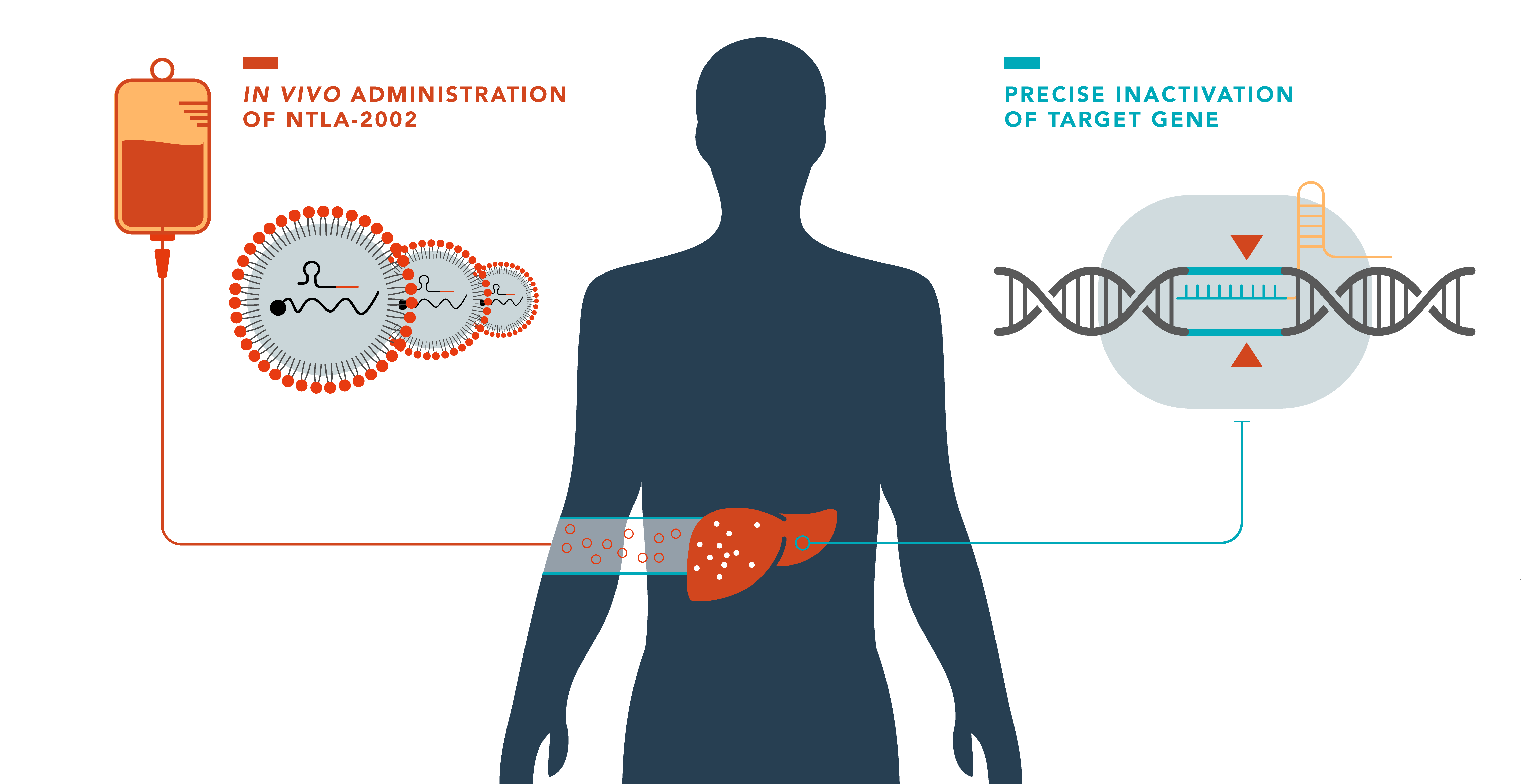
FDA clearance of IND application for NTLA-2001
Intellia announces FDA clearance of Investigational New Drug (IND) application to initiate a pivotal Phase 3 trial of NTLA-2001 for the treatment of transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy.
NTLA-2002 clinical data published in the New England Journal of Medicine
Intellia announces that interim results from the Phase 1 portion of the Phase 1/2 study of NTLA-2002 were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).

NTLA-2002 Phase 2 clinical data published in the New England Journal of Medicine
Results from the Phase 2 study of NTLA-2002 were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the 2024 ACAAI Scientific Meeting.